Big Data/Analytics
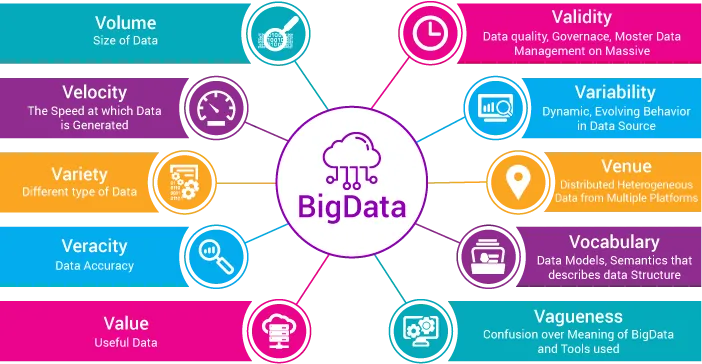
Big Data is a term for very large and complex datasets that exceed the ability of traditional data processing applications to deal with them. Big data technologies include data virtualization, data integration tools (like EMR® and Hadoop®), and search and knowledge discovery tools.
Big Data Analytics examines large and diverse datasets (i.e. big data) to identify patterns, trends, correlations, and other information that lead to insights organizations can harness in support of better decision-making. Big Data Analytics is the science and engineering of problem solving where the nature, size, and shape of the data renders traditional analytics tools difficult or even impossible to use.
Building Blocks of Big Data and Analytics
Analytics – encompasses the discovery, interpretation, and communication of meaningful patterns in data. It relies on the simultaneous application of statistics, computer programming and operations research to quantify performance and is particularly valuable in areas with large amounts of recorded information. Data is cleaned, inspected and modeled to discover useful and actionable information. The analytics flow comprises descriptive, diagnostic, predictive analytics and eventually prescriptive steps.
Business Analytics – describes the skills, technologies, statistical methods and data driven approaches used to explore and investigate past business performance to gain new insights that can support business planning. Examples of business analytics tools include data visualization, business intelligence reporting and big data platforms.
Descriptive, Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics
Descriptive Analytics refers to the analysis of historical data to quantify what happened. The difference between descriptive analytics vs predictive analytics can be illustrated through examples of each: the former could include company reports providing a historic perspective on performance, while the latter considers patterns and trends in past data and applies these to understand what might happen next.
Predictive Analytics describes the practice of using historical data to predict future outcomes. It combines mathematical models (or “predictive algorithms”) with historical data to calculate the likelihood (or degree to which) something will happen. Machine learning based predictive analytics has been around for a while. But until recently it has lacked three key features that are important to drive true marketing value: scale, speed, and application.
Prescriptive Analytics entails the application of mathematical and computational sciences and suggests decision options to take advantage of the results of descriptive and predictive analytics.
Data Platform-Lumada
One of the leading Data Analytics platforms was created by Hitachi to incorporate both OT and IT asset data into a single platform that can compute, analyze and produce insights and actions that improve outcomes.
Key Concepts
Business Intelligence (BI) encompasses the technologies, applications and practices used in the collection, integration, analysis, and presentation of business information to support better business decision-making. The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in big data and business intelligence is already widespread, with companies now using machine-learning algorithms to identify trends and insights in vast quantities of data and make faster real-time decisions. Some examples of these solutions in practice include dashboards, reporting tools, and data discovery tools tied either to a data warehousing tool or to the cloud.
Big Data Visualization refers to techniques that enable users to rapidly understand patterns in big data by presenting it through pictures or graphics. Big data visualization tools can include traditional graphs and pie charts, as well as heat maps, 3D computer models and dendrograms.
Behavioral Analytics – uses data about people’s behavior to understand their intent and predict future actions. The upsurge in consumer data from e-commerce platforms, gaming, web and mobile applications, and the Internet of Things feeds predictive behavioral analytics algorithms that can enable marketing teams to target the right offerings to the right micro-segment at the right time.
Data Mining – is the process of collecting data, aggregating it according to type and sorting through it to identify patterns and predict future trends. An ecommerce company, for example, would use data mining to analyze customer data and give product suggestions through the “customers who bought this item also bought” window. Data mining tools include Tanagra, R and Weka (a suite of machine learning algorithms for data mining).