Data Center
Data centers are centralized locations where computing and networking equipment is concentrated for the purpose of collecting, storing, processing, distributing or allowing access to large amounts of data. They provide important services such as data storage, backup and recovery, data management and networking.
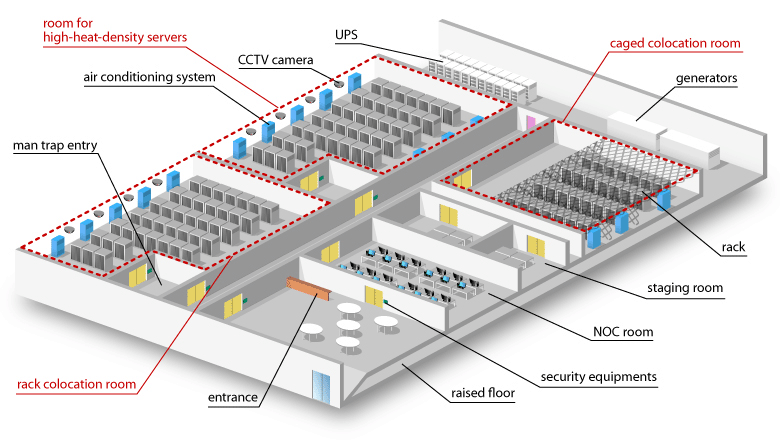
Small Data Center Floor Plan and Functions
The Telecommunication Industry Association developed a data center tier classification standard in 2005 called the TIA-942 project, which identified four categories of data center, rated by metrics like redundancy and level of fault tolerance. These include:
• Tier 1 - Basic site infrastructure with a single distribution path that has no built-in redundancy.
• Tier 2 - Redundant site infrastructure with a single distribution path that includes redundant components.
• Tier 3 - Concurrently maintainable site infrastructure that has multiple paths, only one of which is active at a time.
• Tier 4 - Fault tolerant site infrastructure that has multiple active distribution paths for lots of redundancy.
Data Center Power Components
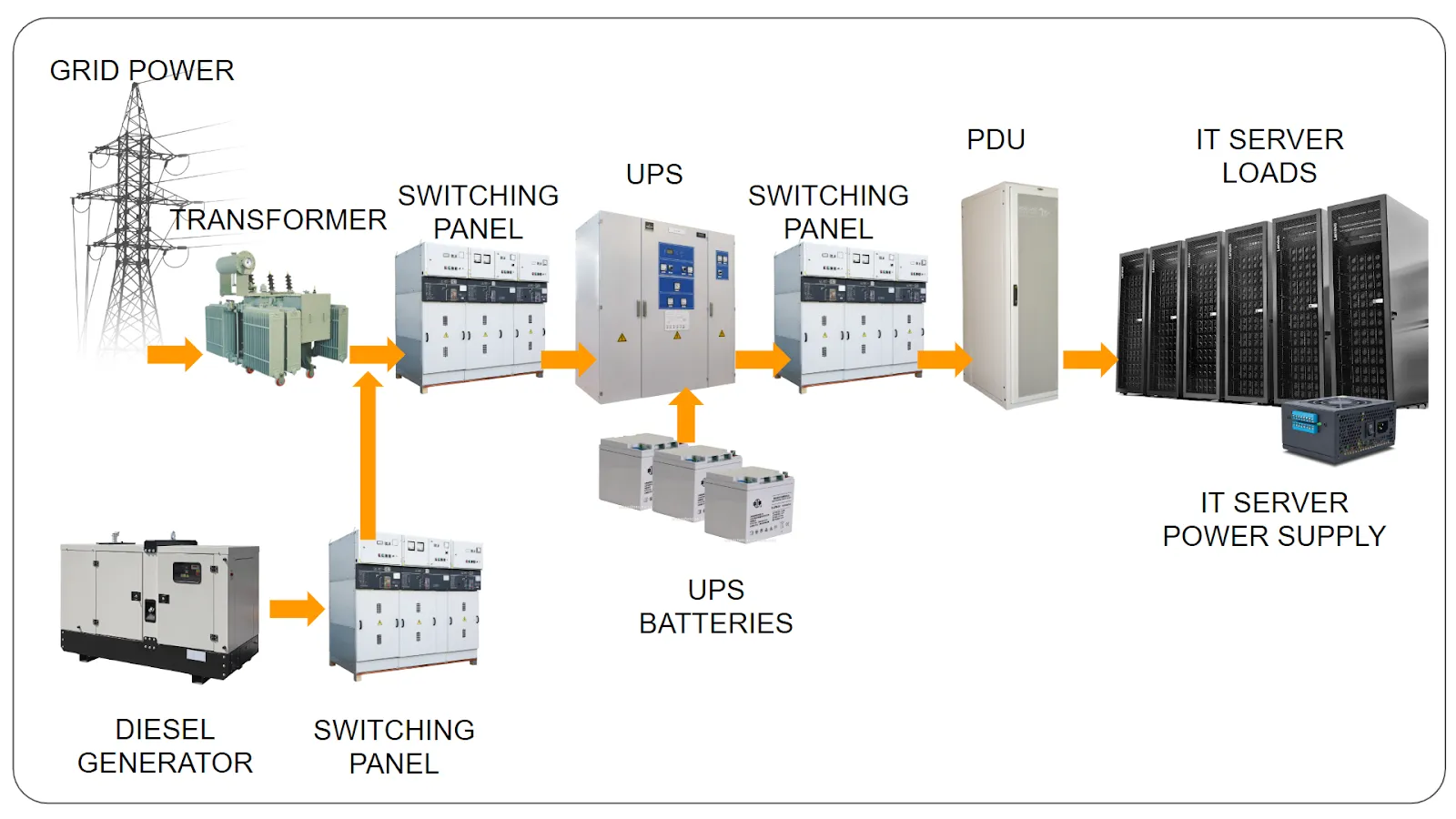
The power supply of every larger data center starts with a connection to the main grid, which is provided by the local utility company. To ensure uninterrupted operation even in the case of a large-scale power outage, data centers are typically connected to at least one diesel or gas backup generator. The electricity from both the local utility company and the backup generator is delivered with a medium voltage and is then transformed by one or more transformers to low voltage.
Switching Panels that house fuses, circuit breakers, and ground leakage protection units, take the low-voltage electricity and distribute it to a number of endpoints, such as Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS) systems or load banks. Additionally, the switching panels manage the incoming power from the main grid and can start the backup generator when they detect a power outage.
Instead of distributing low voltage power directly to sensitive computer electronic components and systems, switching panels pass it through an Uninterrupted Power Supply (UPS) system, which provides short-term power when the input power source fails and protects critical components against voltage spikes, harmonic distortion, and other common power problems.
Most UPS systems are designed to provide power for at least 5 minutes on maximum load during an outage. During those 5 minutes, the backup generation has enough time to make multiple attempts to start and take over the load from the UPS system.
Data Center Network Layer
The core layer provides the interconnection of multiple data center aggregation modules and connects to the core of the campus network; it is required to have high switching capabilities and burst traffic adaptability; the core of large data centers requires the expansion capability of multiple aggregation modules, and small and medium data centers share the core of the campus; current Mainly with 10GE interface.
The aggregation layer provides high-bandwidth export for server farms; it requires high-density GE/10GE ports to achieve access layer interconnection; it has more slots to provide value-added service module deployment. The mainstream practice in the industry is to deploy various security and application optimization services at the convergence layer, such as integrating firewalls, load balancing, and application acceleration boards on switches.
The access layer supports high-density Gigabit access and 10 Gigabit access; the total access bandwidth and uplink bandwidth have convergence ratio and line speed modes; based on rack considerations, 1RU has more flexible deployment capabilities; supports stacking, more Expansion capability; uplink dual link redundancy capability.